
Notes:
HDV is a defective single-stranded RNA virus that requires the helper function of
HBV to replicate. HDV requires HBV for synthesis of envelope protein composed of
HBsAg, which is used to encapsulate the HDV genome.
|
Hepatitis D -
Clinical Features
- Coinfection
- severe acute
disease
- low risk of
chronic infection
- Superinfection
- usually
develop chronic HDV infection high
- risk of
severe chronic liver disease
Notes:
HDV infection can be acquired either as a co-infection with HBV or as a
superinfection of persons with chronic HBV infection. Persons with HBV-HDV
co-infection may have more severe acute disease and a higher risk of fulminant
hepatitis (2%-20%) compared with those infected with HBV alone; however, chronic HBV
infection appears to occur less frequently in persons with HBV-HDV co-infection.
Chronic HBV carriers who acquire HDV superinfection usually develop chronic HDV
infection. In long-term studies of chronic HBV carriers with HDV superinfection,
70%-80% have developed evidence of chronic liver diseases with cirrhosis compared
with 15%-30% of patients with chronic HBV infection alone. |
Hepatitis D
Virus Modes of Transmission
- Percutanous
exposures
- Permucosal
Notes:
The modes of HDV transmission are similar to those for HBV, with percutaneous
exposures the most efficient. Sexual transmission of HDV is less efficient than for
HBV. Perinatal HDV transmission is rare.
|

Notes:
The serologic course of HDV infection varies depending on whether the virus is
acquired as a co-infection with HBV or as a superinfection of a person with chronic
HBV infection. In most persons with HBV-HDV co-infection, both IgM antibody to HDV
(anti-HDV) and IgG anti-HDV are detectable during the course of infection. However,
in about 15% of patients the only evidence of HDV infection may be the detection of
either IgM anti-HDV alone during the early acute period of illness or IgG anti-HDV
alone during convalescence. Anti-HDV generally declines to sub-detectable levels
after the infection resolves and there is no serologic marker that persists to
indicate that the patient was ever infected with HDV. Hepatitis Delta antigen (HDAg)
can be detected in serum in only about 25% of patients with HBV-HDV co-infection.
When HDAg is detectable it generally disappears as HBsAg disappears and most
patients do not develop chronic infection. Tests for IgG anti-HDV are commercially
available in the United States. Tests for IgM anti-HDV, HDAg and HDV RNA by PCR are
only available in research laboratories.
|

Notes:
In patients with chronic HBV infection who are super-infected with HDV several
characteristic serologic features generally occur, including: 1) the titer of HBsAg
declines at the time HDAg appears in the serum, 2) HDAg and HDV RNA remain
detectable in the serum because chronic HDV infection generally occurs in most
patients with HDV superinfection, unlike the case with co-infection, 3) high titers
of both IgM and IgG anti-HDV are detectable, which persist indefinitely.
|
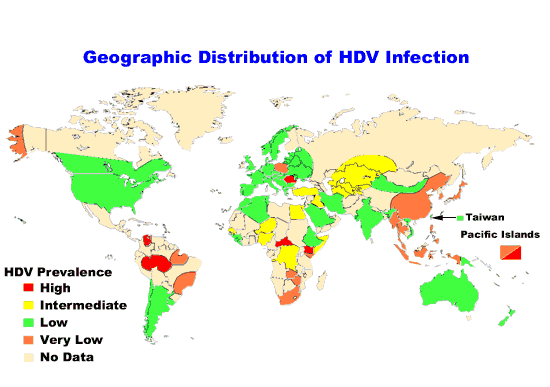
Notes:
In general, the global pattern of HDV infection corresponds to the
prevalence of chronic HBV infection; however, several distinct features of
the distribution of HDV infection have been identified. In countries with a
low prevalence of chronic HBV infection, HDV prevalence is generally low
among both asymptomatic HBV carriers (<10%) and among patients with chronic
HBV-related liver disease (<25%). HDV infection in these countries occurs
most commonly among injecting drug users and persons with hemophilia. In
countries with moderate and high levels of chronic HBV prevalence, the
prevalence of HDV infection is highly variable. In southern Italy and in
parts of Russia and Romania, the prevalence of HDV infection is very high
among both asymptomatic HBV carriers (>20%) and among patients with HBV-related
chronic liver disease HBV (>60%). Other countries, including northern Italy,
Spain, Turkey, and Egypt, have a moderate prevalence of HDV infection among
asymptomatic HBV carriers (10%-19%) and among patients with chronic HBV-related
liver disease (30%-50%). However, in most of Southeast Asia and China, where
the prevalence of chronic HBV infection is very high, HDV infection is
uncommon. In some South American countries in the Amazon River Basin,
periodic epidemics of HDV infection have occurred among chronic HBV carriers
in relatively isolated regions. Disease related to HDV infection in these
outbreaks has been very severe, with rapid progression to fulminant
hepatitis and case-fatality rates of 10%-20%. The cause of the atypical
course of HDV infection in these populations is unknown.
*(Note: The map of anti-HDV prevalence
generalizes available data and patterns may vary within countries.)
|
 |
|
Hepatitis D -
Prevention
- HBV-HDV
Coinfection
Pre or postexposure prophylaxis to prevent
- HBV infection
HBV-HDV Superinfection
Education to reduce risk behaviors among persons with chronic HBV infection
Notes:
Because HDV is dependent on HBV for replication, HBV-HDV co-infection can be
prevented with either pre- or postexposure prophylaxis for HBV. However, no products
exist to prevent HDV superinfection of persons with chronic HBV infection. Thus,
prevention of HDV superinfection depends primarily on education to reduce risk
behaviors.
|
| |
|




